
-
 Español
Español
-
 Portugues
Portugues
-
 Pусский
Pусский
-
 Français
Français
-
 Deutsch
Deutsch
-
 日本語
日本語
-
 한국어
한국어
-
 العربية
العربية
-
 Italiano
Italiano
-
 Nederlands
Nederlands
-
 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά
-
 Svenska
Svenska
-
 Polski
Polski
-
 ไทย
ไทย
-
 Türk dili
Türk dili
-
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी
-
 Indonesia
Indonesia
-
 Melayu
Melayu
-
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
-
 中文
中文
-
 dansk
dansk
-
 Magyar
Magyar
-
 қазақ
қазақ
-
 বাংলা
বাংলা
-
 עִברִית
עִברִית
-
 čeština
čeština
-
 Soomaali
Soomaali
-
 မြန်မာ
မြန်မာ
-
 فارسی
فارسی
-
 українська
українська
-
 norsk
norsk
-
 Gaeilge
Gaeilge
-
 беларускі
беларускі
-
 Română
Română
-
 ພາສາລາວ
ພາສາລາວ
-
 Filipino
Filipino
-
 lietuvių
lietuvių
-
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
-
 македонски
македонски
-
 Suomalainen
Suomalainen
-
 slovenský
slovenský
-
 o'zbek
o'zbek
-
 اردو
اردو
-
 հայերեն
հայերեն
-
 Igbo
Igbo
-
 български
български
-
 سنڌي
سنڌي
-
 Shona
Shona
-
 සිංහල
සිංහල
-
 Hrvatski
Hrvatski
-
 íslenskur
íslenskur
-
 galego
galego
-
 català
català
-
 Zulu South Africa
Zulu South Africa
-
 Afrikaans isiXhosa
Afrikaans isiXhosa
-
 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ
-
 lëtzebuergesch
lëtzebuergesch
-
 Indonésia Sunda
Indonésia Sunda
-
 basa jawa
basa jawa
-
 ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી
-
 Кыргызча
Кыргызча
-
 тоҷикӣ
тоҷикӣ
-
 Србија
Србија
-
 Twi
Twi
-
 Hawaii
Hawaii
-
 Cebu
Cebu
-
 नेपाल
नेपाल
-
 euskara
euskara
-
 Kurdî
Kurdî
-
 frissi
frissi
-
 יידיש
יידיש
-
 latvija
latvija
-
 slovenija
slovenija
-
 kiswahili
kiswahili
-
 ਪੰਜਾਬ
ਪੰਜਾਬ
-
 پښتو
پښتو
-
 საქართველოს
საქართველოს
-
 hua moni
hua moni
-
 bosna
bosna
-
 తెలుగు
తెలుగు
-
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
-
 Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen
-
 Eesti
Eesti
-
 Corsica
Corsica
-
 Yoruba
Yoruba
-
 Gàidhlig na h-Alba
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
-
 Samoa
Samoa
-
 Монгол
Монгол
-
 Hausa
Hausa
-
 Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan
-
 አማራ
አማራ
-
 Shqipëria
Shqipëria
-
 Malagasy
Malagasy
-
 मराठी
मराठी
-
 മലയാളം
മലയാളം
-
 Malta
Malta
-
 ខ្មែរ
ខ្មែរ
-
 Chicheva
Chicheva
-
 中文(繁体)
中文(繁体)
-
 ଓଡିଆ
ଓଡିଆ
-
 Setswana
Setswana
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
-
 Aymara
Aymara
-
 Башҡорт
Башҡорт
-
 Türkmenler
Türkmenler
-
 ትግሪኛ
ትግሪኛ
-
 Afaan Oromoo
Afaan Oromoo
-
 অসমীয়া
অসমীয়া
-
 Kinyarwanda
Kinyarwanda
-
 Ilocano
Ilocano
-
 Wolof
Wolof
-
 अवधी
अवधी
-
 Oluganda
Oluganda
-
 Bikol
Bikol
-
 Fulɓe
Fulɓe
-
 Kikongo
Kikongo
-
 Sango
Sango
-
 ދިވެހި
ދިވެހި
-
 Lingala
Lingala
-
 मैथिली
मैथिली
-
 Tsonga
Tsonga
-
 ꯃꯦꯏ ꯊꯥꯏ꯫
ꯃꯦꯏ ꯊꯥꯏ꯫
-
 brezhoneg
brezhoneg
-
 Furlan
Furlan
-
 नेवा
नेवा
-
 རྫོང་ཁ
རྫོང་ཁ
-
 Santali
Santali
-
 Аҧсуа
Аҧсуа
-
 Нохчийн
Нохчийн
-
 Чӑваш
Чӑваш
-
 Татар
Татар
-
 Batak Karo
Batak Karo
-
 دری
دری
-
 Diura
Diura
-
 Fengyu
Fengyu
-
 Eʋegbe
Eʋegbe
-
 Iban
Iban
-
 Fiji
Fiji
-
 Tonga
Tonga
-
 Inuktitut
Inuktitut
-
 Nahuatl
Nahuatl
-
 maaya yucatec
maaya yucatec
-
 Runasimi
Runasimi
-
 guarani
guarani
-
 Qafar
Qafar
-
 Acholi
Acholi
-
 Dinka
Dinka
-
 Luo
Luo
-
 Lundi
Lundi
-
 isiNdebele
isiNdebele
-
 Tshivenḓa
Tshivenḓa
-
 Sesotho sa Leboa
Sesotho sa Leboa
-
 Sesotho sa Borwa
Sesotho sa Borwa
-
 Ndumbe
Ndumbe
-
 Papuan Pidgin
Papuan Pidgin
-
 Rromani ćhib
Rromani ćhib
-
 Thok Nath
Thok Nath
yuxiatugong@163.com
+86 18353494641
-
 Español
Español
-
 Portugues
Portugues
-
 Pусский
Pусский
-
 Français
Français
-
 Deutsch
Deutsch
-
 日本語
日本語
-
 한국어
한국어
-
 العربية
العربية
-
 Italiano
Italiano
-
 Nederlands
Nederlands
-
 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά
-
 Svenska
Svenska
-
 Polski
Polski
-
 ไทย
ไทย
-
 Türk dili
Türk dili
-
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी
-
 Indonesia
Indonesia
-
 Melayu
Melayu
-
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
-
 中文
中文
-
 dansk
dansk
-
 Magyar
Magyar
-
 қазақ
қазақ
-
 বাংলা
বাংলা
-
 עִברִית
עִברִית
-
 čeština
čeština
-
 Soomaali
Soomaali
-
 မြန်မာ
မြန်မာ
-
 فارسی
فارسی
-
 українська
українська
-
 norsk
norsk
-
 Gaeilge
Gaeilge
-
 беларускі
беларускі
-
 Română
Română
-
 ພາສາລາວ
ພາສາລາວ
-
 Filipino
Filipino
-
 lietuvių
lietuvių
-
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
-
 македонски
македонски
-
 Suomalainen
Suomalainen
-
 slovenský
slovenský
-
 o'zbek
o'zbek
-
 اردو
اردو
-
 հայերեն
հայերեն
-
 Igbo
Igbo
-
 български
български
-
 سنڌي
سنڌي
-
 Shona
Shona
-
 සිංහල
සිංහල
-
 Hrvatski
Hrvatski
-
 íslenskur
íslenskur
-
 galego
galego
-
 català
català
-
 Zulu South Africa
Zulu South Africa
-
 Afrikaans isiXhosa
Afrikaans isiXhosa
-
 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ
-
 lëtzebuergesch
lëtzebuergesch
-
 Indonésia Sunda
Indonésia Sunda
-
 basa jawa
basa jawa
-
 ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી
-
 Кыргызча
Кыргызча
-
 тоҷикӣ
тоҷикӣ
-
 Србија
Србија
-
 Twi
Twi
-
 Hawaii
Hawaii
-
 Cebu
Cebu
-
 नेपाल
नेपाल
-
 euskara
euskara
-
 Kurdî
Kurdî
-
 frissi
frissi
-
 יידיש
יידיש
-
 latvija
latvija
-
 slovenija
slovenija
-
 kiswahili
kiswahili
-
 ਪੰਜਾਬ
ਪੰਜਾਬ
-
 پښتو
پښتو
-
 საქართველოს
საქართველოს
-
 hua moni
hua moni
-
 bosna
bosna
-
 తెలుగు
తెలుగు
-
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
-
 Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen
-
 Eesti
Eesti
-
 Corsica
Corsica
-
 Yoruba
Yoruba
-
 Gàidhlig na h-Alba
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
-
 Samoa
Samoa
-
 Монгол
Монгол
-
 Hausa
Hausa
-
 Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan
-
 አማራ
አማራ
-
 Shqipëria
Shqipëria
-
 Malagasy
Malagasy
-
 मराठी
मराठी
-
 മലയാളം
മലയാളം
-
 Malta
Malta
-
 ខ្មែរ
ខ្មែរ
-
 Chicheva
Chicheva
-
 中文(繁体)
中文(繁体)
-
 ଓଡିଆ
ଓଡିଆ
-
 Setswana
Setswana
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
-
 Aymara
Aymara
-
 Башҡорт
Башҡорт
-
 Türkmenler
Türkmenler
-
 ትግሪኛ
ትግሪኛ
-
 Afaan Oromoo
Afaan Oromoo
-
 অসমীয়া
অসমীয়া
-
 Kinyarwanda
Kinyarwanda
-
 Ilocano
Ilocano
-
 Wolof
Wolof
-
 अवधी
अवधी
-
 Oluganda
Oluganda
-
 Bikol
Bikol
-
 Fulɓe
Fulɓe
-
 Kikongo
Kikongo
-
 Sango
Sango
-
 ދިވެހި
ދިވެހި
-
 Lingala
Lingala
-
 मैथिली
मैथिली
-
 Tsonga
Tsonga
-
 ꯃꯦꯏ ꯊꯥꯏ꯫
ꯃꯦꯏ ꯊꯥꯏ꯫
-
 brezhoneg
brezhoneg
-
 Furlan
Furlan
-
 नेवा
नेवा
-
 རྫོང་ཁ
རྫོང་ཁ
-
 Santali
Santali
-
 Аҧсуа
Аҧсуа
-
 Нохчийн
Нохчийн
-
 Чӑваш
Чӑваш
-
 Татар
Татар
-
 Batak Karo
Batak Karo
-
 دری
دری
-
 Diura
Diura
-
 Fengyu
Fengyu
-
 Eʋegbe
Eʋegbe
-
 Iban
Iban
-
 Fiji
Fiji
-
 Tonga
Tonga
-
 Inuktitut
Inuktitut
-
 Nahuatl
Nahuatl
-
 maaya yucatec
maaya yucatec
-
 Runasimi
Runasimi
-
 guarani
guarani
-
 Qafar
Qafar
-
 Acholi
Acholi
-
 Dinka
Dinka
-
 Luo
Luo
-
 Lundi
Lundi
-
 isiNdebele
isiNdebele
-
 Tshivenḓa
Tshivenḓa
-
 Sesotho sa Leboa
Sesotho sa Leboa
-
 Sesotho sa Borwa
Sesotho sa Borwa
-
 Ndumbe
Ndumbe
-
 Papuan Pidgin
Papuan Pidgin
-
 Rromani ćhib
Rromani ćhib
-
 Thok Nath
Thok Nath

News Center
News Center
HOT PRODUCT
Permeable Filtration Geotextile Fabric for Retaining Wall Drains
2025-10-11 07:55:00
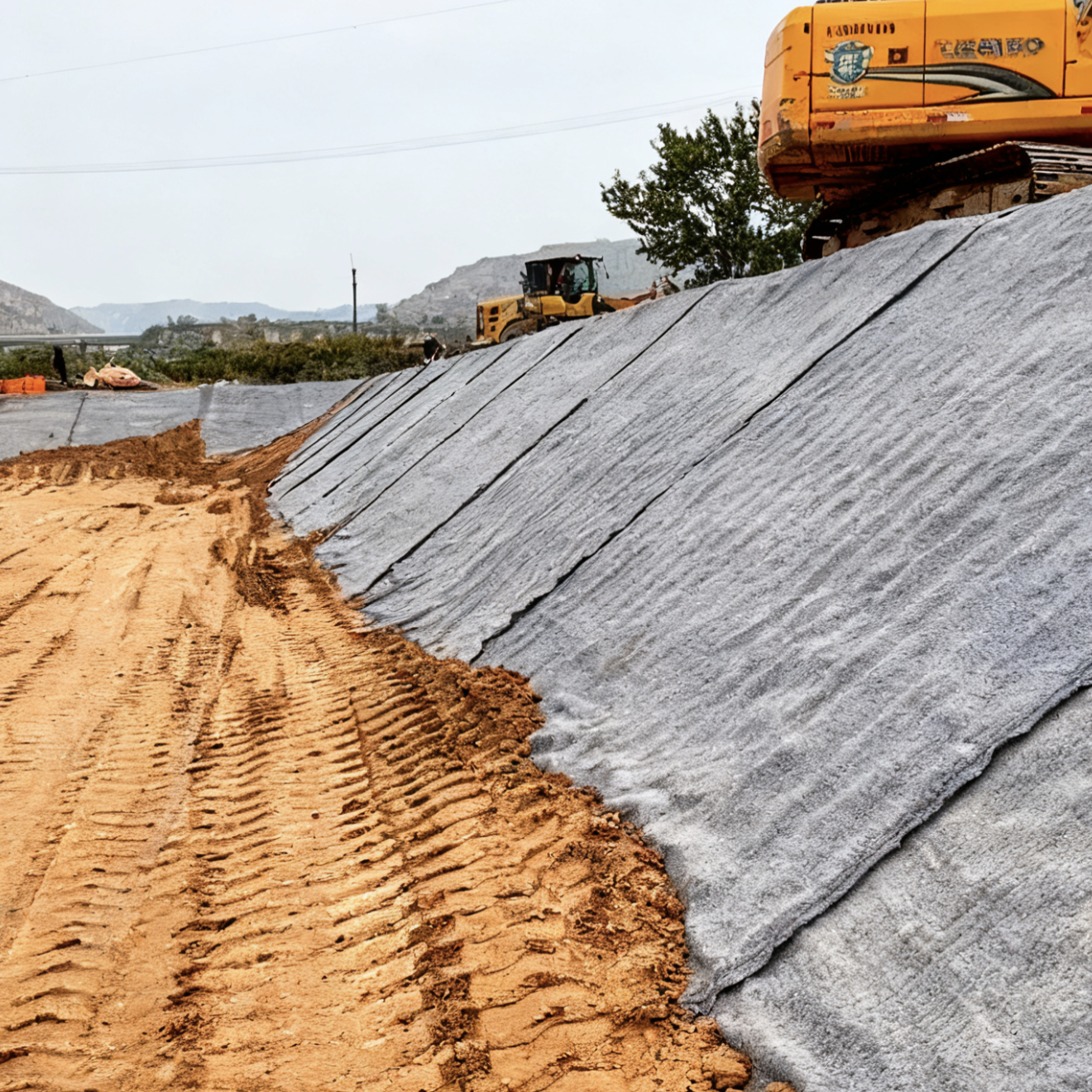

Permeable Filtration Geotextile Fabric for Retaining Wall Drains
Introduction
Retaining walls are essential structures in civil engineering, designed to hold back soil and prevent erosion while maintaining slope stability. One critical component of retaining wall systems is effective drainage, which ensures long-term structural integrity by preventing water buildup and hydrostatic pressure. Permeable filtration geotextile fabrics play a vital role in these drainage systems by allowing water to pass through while retaining soil particles.
This article explores the properties, functions, and applications of permeable geotextile fabrics in retaining wall drainage systems. It also discusses material selection, installation best practices, and performance considerations.
1. Understanding Geotextile Fabrics
Geotextiles are synthetic fabrics engineered for use in civil and environmental applications. They are categorized into woven, non-woven, and knitted types, each with distinct properties suited for different functions such as filtration, separation, reinforcement, and drainage.
1.1 Types of Geotextiles
- Woven Geotextiles: Made by interlacing yarns in a regular pattern, these fabrics offer high tensile strength and are often used for reinforcement.
- Non-Woven Geotextiles: Produced by bonding fibers mechanically, thermally, or chemically, these fabrics excel in filtration and drainage due to their high permeability.
- Knitted Geotextiles: Less common, these are created by interlocking loops of yarn, providing flexibility and moderate strength.
For retaining wall drainage, non-woven geotextiles are typically preferred due to their superior filtration capabilities.
2. Functions of Geotextiles in Retaining Wall Drainage
2.1 Filtration
The primary function of geotextiles in drainage systems is filtration. They allow water to pass through while preventing fine soil particles from clogging the drainage system. This maintains soil stability and prevents erosion.
2.2 Separation
Geotextiles act as a barrier between different soil layers or between soil and aggregate, preventing intermixing that could compromise drainage efficiency.
2.3 Drainage
By facilitating water flow, geotextiles reduce hydrostatic pressure behind retaining walls, preventing structural failure due to water buildup.
2.4 Reinforcement
In some cases, geotextiles provide additional tensile strength to the soil, enhancing the stability of the retaining wall structure.
3. Material Selection for Permeable Filtration Geotextiles
3.1 Polymer Composition
Most geotextiles are made from synthetic polymers such as:
- Polypropylene (PP): Resistant to chemicals and biological degradation, making it ideal for long-term applications.
- Polyester (PET): Offers high strength but is susceptible to hydrolysis in alkaline environments.
3.2 Permeability and Porosity
The fabric must have adequate permeability (measured in liters per square meter per second) to allow water flow while retaining soil particles. The apparent opening size (AOS) determines filtration efficiency.
3.3 Strength and Durability
Geotextiles must withstand installation stresses and long-term environmental exposure, including UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and chemical interactions.
4. Installation Best Practices
4.1 Site Preparation
- Clear the area of debris and sharp objects that could damage the geotextile.
- Ensure proper compaction of the subgrade to prevent differential settlement.
4.2 Placement and Overlap
- Lay the geotextile with sufficient overlap (typically 12-18 inches) to prevent gaps.
- Secure the fabric with staples or pins to prevent movement during backfilling.
4.3 Backfilling
- Use clean, well-graded aggregate to avoid puncturing the fabric.
- Compact the backfill material in layers to minimize stress on the geotextile.
5. Performance Considerations
5.1 Clogging Resistance
The geotextile must balance filtration efficiency with permeability to avoid clogging over time. Proper selection of AOS and fabric type is crucial.
5.2 Long-Term Durability
Exposure to harsh conditions (e.g., high pH soils, UV radiation) can degrade geotextiles. UV-stabilized fabrics or protective covers may be necessary.
5.3 Hydraulic Performance
Regular inspections should ensure that the geotextile continues to facilitate proper drainage without excessive clogging or degradation.
6. Applications Beyond Retaining Walls
Permeable geotextiles are also used in:
- Road and railway construction (for subgrade stabilization).
- Landfill liners and caps (for filtration and separation).
- Erosion control (in slopes and shorelines).
7. Conclusion
Permeable filtration geotextile fabrics are indispensable in retaining wall drainage systems, ensuring long-term stability by managing water flow and preventing soil erosion. Proper material selection, installation, and maintenance are critical to maximizing performance. Engineers and contractors must carefully evaluate project-specific requirements to choose the most suitable geotextile, ensuring durability and efficiency in drainage applications.
By understanding the key properties and functions of geotextiles, professionals can design and construct retaining walls that withstand environmental challenges while maintaining structural integrity for decades.
---
This article provides a comprehensive overview of permeable geotextile fabrics in retaining wall drainage without referencing any specific company or brand. Let me know if you'd like any modifications or additional details!








 Phone
Phone
Comment
(0)