
-
 Español
Español
-
 Portugues
Portugues
-
 Pусский
Pусский
-
 Français
Français
-
 Deutsch
Deutsch
-
 日本語
日本語
-
 한국어
한국어
-
 العربية
العربية
-
 Italiano
Italiano
-
 Nederlands
Nederlands
-
 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά
-
 Svenska
Svenska
-
 Polski
Polski
-
 ไทย
ไทย
-
 Türk dili
Türk dili
-
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी
-
 Indonesia
Indonesia
-
 Melayu
Melayu
-
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
-
 中文
中文
-
 dansk
dansk
-
 Magyar
Magyar
-
 қазақ
қазақ
-
 বাংলা
বাংলা
-
 עִברִית
עִברִית
-
 čeština
čeština
-
 Soomaali
Soomaali
-
 မြန်မာ
မြန်မာ
-
 فارسی
فارسی
-
 українська
українська
-
 norsk
norsk
-
 Gaeilge
Gaeilge
-
 беларускі
беларускі
-
 Română
Română
-
 ພາສາລາວ
ພາສາລາວ
-
 Filipino
Filipino
-
 lietuvių
lietuvių
-
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
-
 македонски
македонски
-
 Suomalainen
Suomalainen
-
 slovenský
slovenský
-
 o'zbek
o'zbek
-
 اردو
اردو
-
 հայերեն
հայերեն
-
 Igbo
Igbo
-
 български
български
-
 سنڌي
سنڌي
-
 Shona
Shona
-
 සිංහල
සිංහල
-
 Hrvatski
Hrvatski
-
 íslenskur
íslenskur
-
 galego
galego
-
 català
català
-
 Zulu South Africa
Zulu South Africa
-
 Afrikaans isiXhosa
Afrikaans isiXhosa
-
 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ
-
 lëtzebuergesch
lëtzebuergesch
-
 Indonésia Sunda
Indonésia Sunda
-
 basa jawa
basa jawa
-
 ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી
-
 Кыргызча
Кыргызча
-
 тоҷикӣ
тоҷикӣ
-
 Србија
Србија
-
 Twi
Twi
-
 Hawaii
Hawaii
-
 Cebu
Cebu
-
 नेपाल
नेपाल
-
 euskara
euskara
-
 Kurdî
Kurdî
-
 frissi
frissi
-
 יידיש
יידיש
-
 latvija
latvija
-
 slovenija
slovenija
-
 kiswahili
kiswahili
-
 ਪੰਜਾਬ
ਪੰਜਾਬ
-
 پښتو
پښتو
-
 საქართველოს
საქართველოს
-
 hua moni
hua moni
-
 bosna
bosna
-
 తెలుగు
తెలుగు
-
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
-
 Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen
-
 Eesti
Eesti
-
 Corsica
Corsica
-
 Yoruba
Yoruba
-
 Gàidhlig na h-Alba
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
-
 Samoa
Samoa
-
 Монгол
Монгол
-
 Hausa
Hausa
-
 Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan
-
 አማራ
አማራ
-
 Shqipëria
Shqipëria
-
 Malagasy
Malagasy
-
 मराठी
मराठी
-
 മലയാളം
മലയാളം
-
 Malta
Malta
-
 ខ្មែរ
ខ្មែរ
-
 Chicheva
Chicheva
-
 中文(繁体)
中文(繁体)
-
 ଓଡିଆ
ଓଡିଆ
-
 Setswana
Setswana
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
-
 Aymara
Aymara
-
 Башҡорт
Башҡорт
-
 Türkmenler
Türkmenler
-
 ትግሪኛ
ትግሪኛ
-
 Afaan Oromoo
Afaan Oromoo
-
 অসমীয়া
অসমীয়া
-
 Kinyarwanda
Kinyarwanda
-
 Ilocano
Ilocano
-
 Wolof
Wolof
-
 अवधी
अवधी
-
 Oluganda
Oluganda
-
 Bikol
Bikol
-
 Fulɓe
Fulɓe
-
 Kikongo
Kikongo
-
 Sango
Sango
-
 ދިވެހި
ދިވެހި
-
 Lingala
Lingala
-
 मैथिली
मैथिली
-
 Tsonga
Tsonga
-
 ꯃꯦꯏ ꯊꯥꯏ꯫
ꯃꯦꯏ ꯊꯥꯏ꯫
-
 brezhoneg
brezhoneg
-
 Furlan
Furlan
-
 नेवा
नेवा
-
 རྫོང་ཁ
རྫོང་ཁ
-
 Santali
Santali
-
 Аҧсуа
Аҧсуа
-
 Нохчийн
Нохчийн
-
 Чӑваш
Чӑваш
-
 Татар
Татар
-
 Batak Karo
Batak Karo
-
 دری
دری
-
 Diura
Diura
-
 Fengyu
Fengyu
-
 Eʋegbe
Eʋegbe
-
 Iban
Iban
-
 Fiji
Fiji
-
 Tonga
Tonga
-
 Inuktitut
Inuktitut
-
 Nahuatl
Nahuatl
-
 maaya yucatec
maaya yucatec
-
 Runasimi
Runasimi
-
 guarani
guarani
-
 Qafar
Qafar
-
 Acholi
Acholi
-
 Dinka
Dinka
-
 Luo
Luo
-
 Lundi
Lundi
-
 isiNdebele
isiNdebele
-
 Tshivenḓa
Tshivenḓa
-
 Sesotho sa Leboa
Sesotho sa Leboa
-
 Sesotho sa Borwa
Sesotho sa Borwa
-
 Ndumbe
Ndumbe
-
 Papuan Pidgin
Papuan Pidgin
-
 Rromani ćhib
Rromani ćhib
-
 Thok Nath
Thok Nath
yuxiatugong@163.com
+86 18353494641
-
 Español
Español
-
 Portugues
Portugues
-
 Pусский
Pусский
-
 Français
Français
-
 Deutsch
Deutsch
-
 日本語
日本語
-
 한국어
한국어
-
 العربية
العربية
-
 Italiano
Italiano
-
 Nederlands
Nederlands
-
 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά
-
 Svenska
Svenska
-
 Polski
Polski
-
 ไทย
ไทย
-
 Türk dili
Türk dili
-
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी
-
 Indonesia
Indonesia
-
 Melayu
Melayu
-
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
-
 中文
中文
-
 dansk
dansk
-
 Magyar
Magyar
-
 қазақ
қазақ
-
 বাংলা
বাংলা
-
 עִברִית
עִברִית
-
 čeština
čeština
-
 Soomaali
Soomaali
-
 မြန်မာ
မြန်မာ
-
 فارسی
فارسی
-
 українська
українська
-
 norsk
norsk
-
 Gaeilge
Gaeilge
-
 беларускі
беларускі
-
 Română
Română
-
 ພາສາລາວ
ພາສາລາວ
-
 Filipino
Filipino
-
 lietuvių
lietuvių
-
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
-
 македонски
македонски
-
 Suomalainen
Suomalainen
-
 slovenský
slovenský
-
 o'zbek
o'zbek
-
 اردو
اردو
-
 հայերեն
հայերեն
-
 Igbo
Igbo
-
 български
български
-
 سنڌي
سنڌي
-
 Shona
Shona
-
 සිංහල
සිංහල
-
 Hrvatski
Hrvatski
-
 íslenskur
íslenskur
-
 galego
galego
-
 català
català
-
 Zulu South Africa
Zulu South Africa
-
 Afrikaans isiXhosa
Afrikaans isiXhosa
-
 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ
-
 lëtzebuergesch
lëtzebuergesch
-
 Indonésia Sunda
Indonésia Sunda
-
 basa jawa
basa jawa
-
 ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી
-
 Кыргызча
Кыргызча
-
 тоҷикӣ
тоҷикӣ
-
 Србија
Србија
-
 Twi
Twi
-
 Hawaii
Hawaii
-
 Cebu
Cebu
-
 नेपाल
नेपाल
-
 euskara
euskara
-
 Kurdî
Kurdî
-
 frissi
frissi
-
 יידיש
יידיש
-
 latvija
latvija
-
 slovenija
slovenija
-
 kiswahili
kiswahili
-
 ਪੰਜਾਬ
ਪੰਜਾਬ
-
 پښتو
پښتو
-
 საქართველოს
საქართველოს
-
 hua moni
hua moni
-
 bosna
bosna
-
 తెలుగు
తెలుగు
-
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
-
 Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen
-
 Eesti
Eesti
-
 Corsica
Corsica
-
 Yoruba
Yoruba
-
 Gàidhlig na h-Alba
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
-
 Samoa
Samoa
-
 Монгол
Монгол
-
 Hausa
Hausa
-
 Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan
-
 አማራ
አማራ
-
 Shqipëria
Shqipëria
-
 Malagasy
Malagasy
-
 मराठी
मराठी
-
 മലയാളം
മലയാളം
-
 Malta
Malta
-
 ខ្មែរ
ខ្មែរ
-
 Chicheva
Chicheva
-
 中文(繁体)
中文(繁体)
-
 ଓଡିଆ
ଓଡିଆ
-
 Setswana
Setswana
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
-
 Aymara
Aymara
-
 Башҡорт
Башҡорт
-
 Türkmenler
Türkmenler
-
 ትግሪኛ
ትግሪኛ
-
 Afaan Oromoo
Afaan Oromoo
-
 অসমীয়া
অসমীয়া
-
 Kinyarwanda
Kinyarwanda
-
 Ilocano
Ilocano
-
 Wolof
Wolof
-
 अवधी
अवधी
-
 Oluganda
Oluganda
-
 Bikol
Bikol
-
 Fulɓe
Fulɓe
-
 Kikongo
Kikongo
-
 Sango
Sango
-
 ދިވެހި
ދިވެހި
-
 Lingala
Lingala
-
 मैथिली
मैथिली
-
 Tsonga
Tsonga
-
 ꯃꯦꯏ ꯊꯥꯏ꯫
ꯃꯦꯏ ꯊꯥꯏ꯫
-
 brezhoneg
brezhoneg
-
 Furlan
Furlan
-
 नेवा
नेवा
-
 རྫོང་ཁ
རྫོང་ཁ
-
 Santali
Santali
-
 Аҧсуа
Аҧсуа
-
 Нохчийн
Нохчийн
-
 Чӑваш
Чӑваш
-
 Татар
Татар
-
 Batak Karo
Batak Karo
-
 دری
دری
-
 Diura
Diura
-
 Fengyu
Fengyu
-
 Eʋegbe
Eʋegbe
-
 Iban
Iban
-
 Fiji
Fiji
-
 Tonga
Tonga
-
 Inuktitut
Inuktitut
-
 Nahuatl
Nahuatl
-
 maaya yucatec
maaya yucatec
-
 Runasimi
Runasimi
-
 guarani
guarani
-
 Qafar
Qafar
-
 Acholi
Acholi
-
 Dinka
Dinka
-
 Luo
Luo
-
 Lundi
Lundi
-
 isiNdebele
isiNdebele
-
 Tshivenḓa
Tshivenḓa
-
 Sesotho sa Leboa
Sesotho sa Leboa
-
 Sesotho sa Borwa
Sesotho sa Borwa
-
 Ndumbe
Ndumbe
-
 Papuan Pidgin
Papuan Pidgin
-
 Rromani ćhib
Rromani ćhib
-
 Thok Nath
Thok Nath

News Center
News Center
HOT PRODUCT
Filtration Geotextile Fabric for Stormwater Management
2025-10-16 08:01:27
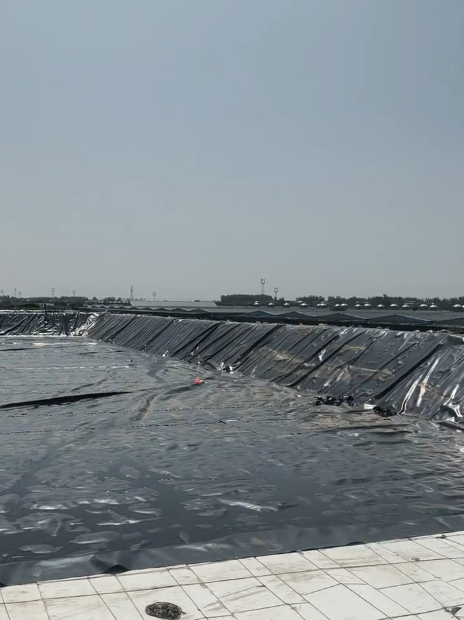

Filtration Geotextile Fabric for Stormwater Management
Introduction
Stormwater management is a critical aspect of urban and rural infrastructure development, ensuring the proper drainage of rainwater while minimizing environmental impact. One of the key components in modern stormwater management systems is filtration geotextile fabric, a permeable textile material designed to separate, filter, reinforce, protect, or drain water in various civil engineering applications.
This paper explores the role of filtration geotextile fabric in stormwater management, discussing its properties, functions, applications, and benefits. Additionally, it examines the selection criteria, installation methods, and long-term performance considerations to ensure effective stormwater control.
---
1. What is Filtration Geotextile Fabric?
Filtration geotextile fabric is a synthetic material made from polymers such as polypropylene or polyester. It is engineered to allow water to pass through while retaining soil particles, preventing clogging in drainage systems. Geotextiles can be woven, non-woven, or knitted, with each type offering distinct filtration and permeability characteristics.
1.1 Types of Geotextiles Used in Stormwater Management
- Non-woven geotextiles: Made by bonding fibers mechanically, thermally, or chemically, these fabrics are highly permeable and ideal for filtration and separation.
- Woven geotextiles: Manufactured by weaving yarns together, these fabrics provide high tensile strength and are often used in reinforcement applications.
- Knitted geotextiles: Less common but used in specialized applications requiring flexibility and durability.
1.2 Key Properties of Filtration Geotextiles
- Permeability: Allows water to flow while retaining fine soil particles.
- Filtration efficiency: Prevents soil migration while maintaining drainage.
- Durability: Resistant to UV degradation, chemicals, and biological factors.
- Tensile strength: Withstands mechanical stresses during installation and use.
- Puncture resistance: Protects against damage from sharp objects.
---
2. Functions of Geotextile Fabric in Stormwater Management
Filtration geotextile fabric serves multiple functions in stormwater management systems:
2.1 Separation
Geotextiles prevent the mixing of different soil layers, such as subgrade soil and aggregate, ensuring long-term structural stability in drainage systems.
2.2 Filtration
By allowing water to pass while retaining soil particles, geotextiles prevent clogging in stormwater pipes, retention ponds, and infiltration systems.
2.3 Drainage
Geotextiles enhance water flow in subsurface drainage systems, reducing hydrostatic pressure and preventing waterlogging.
2.4 Protection
They act as a cushioning layer, protecting geomembranes and other waterproofing materials from punctures and abrasion.
2.5 Reinforcement
In some applications, geotextiles provide additional strength to soil structures, such as embankments and retaining walls.
---
3. Applications in Stormwater Management
Filtration geotextile fabric is widely used in various stormwater management systems, including:
3.1 French Drains and Subsurface Drainage
Geotextiles wrap around perforated pipes and gravel layers to prevent soil infiltration while allowing water to drain efficiently.
3.2 Retention and Detention Ponds
They line ponds to filter sediment and prevent erosion while maintaining water flow.
3.3 Permeable Pavements
Installed beneath permeable pavers or porous asphalt, geotextiles enhance filtration and prevent soil migration.
3.4 Green Roofs and Rain Gardens
Geotextiles support vegetation while ensuring proper drainage and preventing soil loss.
3.5 Erosion Control
Used in slope stabilization and riprap applications, geotextiles reduce soil erosion caused by stormwater runoff.
3.6 Infiltration Trenches
They facilitate groundwater recharge by filtering stormwater before it enters the soil.
---
4. Selection Criteria for Filtration Geotextiles
Choosing the right geotextile for stormwater management depends on several factors:
4.1 Hydraulic Properties
- Permeability (k): Must match the expected water flow rate.
- Porosity: Affects filtration efficiency.
- Apparent Opening Size (AOS): Determines the size of particles retained.
4.2 Mechanical Properties
- Grab tensile strength: Resistance to pulling forces.
- Puncture resistance: Ability to withstand sharp objects.
- Elongation at break: Flexibility under stress.
4.3 Environmental Conditions
- UV resistance: Important for exposed applications.
- Chemical resistance: Must withstand pH variations and pollutants.
- Biological resistance: Should not degrade due to microbial activity.
4.4 Installation Requirements
- Roll size and weight: Affects handling and placement.
- Seaming methods: Ensures proper overlap and joint integrity.
---
5. Installation Best Practices
Proper installation is crucial for the effectiveness of geotextile fabric in stormwater management:
5.1 Site Preparation
- Clear debris and level the surface.
- Compact subgrade soil if necessary.
5.2 Geotextile Placement
- Unroll the fabric smoothly without wrinkles.
- Overlap adjacent rolls by at least 12 inches (30 cm).
- Secure edges with staples or stakes to prevent movement.
5.3 Covering with Aggregate or Soil
- Place drainage stone or soil carefully to avoid punctures.
- Avoid heavy machinery directly on the geotextile.
5.4 Seaming and Jointing
- Use sewing, heat bonding, or adhesive for seams.
- Ensure continuous coverage without gaps.
---
6. Long-Term Performance and Maintenance
6.1 Durability Considerations
- UV degradation: Covered geotextiles last longer than exposed ones.
- Clogging potential: Proper AOS selection minimizes clogging.
- Chemical stability: Must resist degradation from stormwater pollutants.
6.2 Inspection and Maintenance
- Regularly check for sediment buildup.
- Clean or replace geotextiles in high-clogging environments.
- Monitor for signs of tearing or displacement.
---
7. Environmental and Economic Benefits
7.1 Environmental Advantages
- Reduces sediment pollution in waterways.
- Enhances groundwater recharge.
- Supports sustainable stormwater solutions like green infrastructure.
7.2 Cost-Effectiveness
- Extends the lifespan of drainage systems.
- Reduces maintenance costs by preventing clogging.
- Minimizes erosion-related repairs.
---
8. Challenges and Limitations
Despite their benefits, filtration geotextiles have some limitations:
- Improper selection can lead to clogging or inadequate filtration.
- Poor installation reduces effectiveness.
- Long-term performance depends on environmental conditions.
---
9. Future Trends in Geotextile Technology
Advancements in geotextile materials include:
- Biodegradable geotextiles for eco-friendly applications.
- Smart geotextiles with sensors for real-time monitoring.
- Nanofiber-enhanced fabrics for improved filtration.
---
10. Conclusion
Filtration geotextile fabric plays a vital role in modern stormwater management by providing separation, filtration, drainage, and protection. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance ensure long-term performance, contributing to sustainable water management practices. As technology advances, geotextiles will continue to evolve, offering even more efficient and environmentally friendly solutions for stormwater control.
By integrating geotextiles into stormwater infrastructure, engineers and planners can enhance system durability, reduce environmental impact, and improve water quality—making them an indispensable component of sustainable urban and rural development.
- Previous page: Durable Mining Composite Geomembrane Puncture Resistant
- Next page: HDPE Pond Lining Composite Geomembrane for Fish Ponds








 Phone
Phone
Comment
(0)