
-
 Español
Español
-
 Portugues
Portugues
-
 Pусский
Pусский
-
 Français
Français
-
 Deutsch
Deutsch
-
 日本語
日本語
-
 한국어
한국어
-
 العربية
العربية
-
 Italiano
Italiano
-
 Nederlands
Nederlands
-
 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά
-
 Svenska
Svenska
-
 Polski
Polski
-
 ไทย
ไทย
-
 Türk dili
Türk dili
-
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी
-
 Indonesia
Indonesia
-
 Melayu
Melayu
-
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
-
 中文
中文
-
 dansk
dansk
-
 Magyar
Magyar
-
 қазақ
қазақ
-
 বাংলা
বাংলা
-
 עִברִית
עִברִית
-
 čeština
čeština
-
 Soomaali
Soomaali
-
 မြန်မာ
မြန်မာ
-
 فارسی
فارسی
-
 українська
українська
-
 norsk
norsk
-
 Gaeilge
Gaeilge
-
 беларускі
беларускі
-
 Română
Română
-
 ພາສາລາວ
ພາສາລາວ
-
 Filipino
Filipino
-
 lietuvių
lietuvių
-
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
-
 македонски
македонски
-
 Suomalainen
Suomalainen
-
 slovenský
slovenský
-
 o'zbek
o'zbek
-
 اردو
اردو
-
 հայերեն
հայերեն
-
 Igbo
Igbo
-
 български
български
-
 سنڌي
سنڌي
-
 Shona
Shona
-
 සිංහල
සිංහල
-
 Hrvatski
Hrvatski
-
 íslenskur
íslenskur
-
 galego
galego
-
 català
català
-
 Zulu South Africa
Zulu South Africa
-
 Afrikaans isiXhosa
Afrikaans isiXhosa
-
 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ
-
 lëtzebuergesch
lëtzebuergesch
-
 Indonésia Sunda
Indonésia Sunda
-
 basa jawa
basa jawa
-
 ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી
-
 Кыргызча
Кыргызча
-
 тоҷикӣ
тоҷикӣ
-
 Србија
Србија
-
 Twi
Twi
-
 Hawaii
Hawaii
-
 Cebu
Cebu
-
 नेपाल
नेपाल
-
 euskara
euskara
-
 Kurdî
Kurdî
-
 frissi
frissi
-
 יידיש
יידיש
-
 latvija
latvija
-
 slovenija
slovenija
-
 kiswahili
kiswahili
-
 ਪੰਜਾਬ
ਪੰਜਾਬ
-
 پښتو
پښتو
-
 საქართველოს
საქართველოს
-
 hua moni
hua moni
-
 bosna
bosna
-
 తెలుగు
తెలుగు
-
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
-
 Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen
-
 Eesti
Eesti
-
 Corsica
Corsica
-
 Yoruba
Yoruba
-
 Gàidhlig na h-Alba
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
-
 Samoa
Samoa
-
 Монгол
Монгол
-
 Hausa
Hausa
-
 Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan
-
 አማራ
አማራ
-
 Shqipëria
Shqipëria
-
 Malagasy
Malagasy
-
 मराठी
मराठी
-
 മലയാളം
മലയാളം
-
 Malta
Malta
-
 ខ្មែរ
ខ្មែរ
-
 Chicheva
Chicheva
-
 中文(繁体)
中文(繁体)
-
 ଓଡିଆ
ଓଡିଆ
-
 Setswana
Setswana
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
-
 Aymara
Aymara
-
 Башҡорт
Башҡорт
-
 Türkmenler
Türkmenler
-
 ትግሪኛ
ትግሪኛ
-
 Afaan Oromoo
Afaan Oromoo
-
 অসমীয়া
অসমীয়া
-
 Kinyarwanda
Kinyarwanda
-
 Ilocano
Ilocano
-
 Wolof
Wolof
-
 अवधी
अवधी
-
 Oluganda
Oluganda
-
 Bikol
Bikol
-
 Fulɓe
Fulɓe
-
 Kikongo
Kikongo
-
 Sango
Sango
-
 ދިވެހި
ދިވެހި
-
 Lingala
Lingala
-
 मैथिली
मैथिली
-
 Tsonga
Tsonga
-
 ꯃꯦꯏ ꯊꯥꯏ꯫
ꯃꯦꯏ ꯊꯥꯏ꯫
-
 brezhoneg
brezhoneg
-
 Furlan
Furlan
-
 नेवा
नेवा
-
 རྫོང་ཁ
རྫོང་ཁ
-
 Santali
Santali
-
 Аҧсуа
Аҧсуа
-
 Нохчийн
Нохчийн
-
 Чӑваш
Чӑваш
-
 Татар
Татар
-
 Batak Karo
Batak Karo
-
 دری
دری
-
 Diura
Diura
-
 Fengyu
Fengyu
-
 Eʋegbe
Eʋegbe
-
 Iban
Iban
-
 Fiji
Fiji
-
 Tonga
Tonga
-
 Inuktitut
Inuktitut
-
 Nahuatl
Nahuatl
-
 maaya yucatec
maaya yucatec
-
 Runasimi
Runasimi
-
 guarani
guarani
-
 Qafar
Qafar
-
 Acholi
Acholi
-
 Dinka
Dinka
-
 Luo
Luo
-
 Lundi
Lundi
-
 isiNdebele
isiNdebele
-
 Tshivenḓa
Tshivenḓa
-
 Sesotho sa Leboa
Sesotho sa Leboa
-
 Sesotho sa Borwa
Sesotho sa Borwa
-
 Ndumbe
Ndumbe
-
 Papuan Pidgin
Papuan Pidgin
-
 Rromani ćhib
Rromani ćhib
-
 Thok Nath
Thok Nath
yuxiatugong@163.com
+86 18353494641
-
 Español
Español
-
 Portugues
Portugues
-
 Pусский
Pусский
-
 Français
Français
-
 Deutsch
Deutsch
-
 日本語
日本語
-
 한국어
한국어
-
 العربية
العربية
-
 Italiano
Italiano
-
 Nederlands
Nederlands
-
 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά
-
 Svenska
Svenska
-
 Polski
Polski
-
 ไทย
ไทย
-
 Türk dili
Türk dili
-
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी
-
 Indonesia
Indonesia
-
 Melayu
Melayu
-
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
-
 中文
中文
-
 dansk
dansk
-
 Magyar
Magyar
-
 қазақ
қазақ
-
 বাংলা
বাংলা
-
 עִברִית
עִברִית
-
 čeština
čeština
-
 Soomaali
Soomaali
-
 မြန်မာ
မြန်မာ
-
 فارسی
فارسی
-
 українська
українська
-
 norsk
norsk
-
 Gaeilge
Gaeilge
-
 беларускі
беларускі
-
 Română
Română
-
 ພາສາລາວ
ພາສາລາວ
-
 Filipino
Filipino
-
 lietuvių
lietuvių
-
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
-
 македонски
македонски
-
 Suomalainen
Suomalainen
-
 slovenský
slovenský
-
 o'zbek
o'zbek
-
 اردو
اردو
-
 հայերեն
հայերեն
-
 Igbo
Igbo
-
 български
български
-
 سنڌي
سنڌي
-
 Shona
Shona
-
 සිංහල
සිංහල
-
 Hrvatski
Hrvatski
-
 íslenskur
íslenskur
-
 galego
galego
-
 català
català
-
 Zulu South Africa
Zulu South Africa
-
 Afrikaans isiXhosa
Afrikaans isiXhosa
-
 ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ
-
 lëtzebuergesch
lëtzebuergesch
-
 Indonésia Sunda
Indonésia Sunda
-
 basa jawa
basa jawa
-
 ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી
-
 Кыргызча
Кыргызча
-
 тоҷикӣ
тоҷикӣ
-
 Србија
Србија
-
 Twi
Twi
-
 Hawaii
Hawaii
-
 Cebu
Cebu
-
 नेपाल
नेपाल
-
 euskara
euskara
-
 Kurdî
Kurdî
-
 frissi
frissi
-
 יידיש
יידיש
-
 latvija
latvija
-
 slovenija
slovenija
-
 kiswahili
kiswahili
-
 ਪੰਜਾਬ
ਪੰਜਾਬ
-
 پښتو
پښتو
-
 საქართველოს
საქართველოს
-
 hua moni
hua moni
-
 bosna
bosna
-
 తెలుగు
తెలుగు
-
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
-
 Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen
-
 Eesti
Eesti
-
 Corsica
Corsica
-
 Yoruba
Yoruba
-
 Gàidhlig na h-Alba
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
-
 Samoa
Samoa
-
 Монгол
Монгол
-
 Hausa
Hausa
-
 Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan
-
 አማራ
አማራ
-
 Shqipëria
Shqipëria
-
 Malagasy
Malagasy
-
 मराठी
मराठी
-
 മലയാളം
മലയാളം
-
 Malta
Malta
-
 ខ្មែរ
ខ្មែរ
-
 Chicheva
Chicheva
-
 中文(繁体)
中文(繁体)
-
 ଓଡିଆ
ଓଡିଆ
-
 Setswana
Setswana
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
-
 Aymara
Aymara
-
 Башҡорт
Башҡорт
-
 Türkmenler
Türkmenler
-
 ትግሪኛ
ትግሪኛ
-
 Afaan Oromoo
Afaan Oromoo
-
 অসমীয়া
অসমীয়া
-
 Kinyarwanda
Kinyarwanda
-
 Ilocano
Ilocano
-
 Wolof
Wolof
-
 अवधी
अवधी
-
 Oluganda
Oluganda
-
 Bikol
Bikol
-
 Fulɓe
Fulɓe
-
 Kikongo
Kikongo
-
 Sango
Sango
-
 ދިވެހި
ދިވެހި
-
 Lingala
Lingala
-
 मैथिली
मैथिली
-
 Tsonga
Tsonga
-
 ꯃꯦꯏ ꯊꯥꯏ꯫
ꯃꯦꯏ ꯊꯥꯏ꯫
-
 brezhoneg
brezhoneg
-
 Furlan
Furlan
-
 नेवा
नेवा
-
 རྫོང་ཁ
རྫོང་ཁ
-
 Santali
Santali
-
 Аҧсуа
Аҧсуа
-
 Нохчийн
Нохчийн
-
 Чӑваш
Чӑваш
-
 Татар
Татар
-
 Batak Karo
Batak Karo
-
 دری
دری
-
 Diura
Diura
-
 Fengyu
Fengyu
-
 Eʋegbe
Eʋegbe
-
 Iban
Iban
-
 Fiji
Fiji
-
 Tonga
Tonga
-
 Inuktitut
Inuktitut
-
 Nahuatl
Nahuatl
-
 maaya yucatec
maaya yucatec
-
 Runasimi
Runasimi
-
 guarani
guarani
-
 Qafar
Qafar
-
 Acholi
Acholi
-
 Dinka
Dinka
-
 Luo
Luo
-
 Lundi
Lundi
-
 isiNdebele
isiNdebele
-
 Tshivenḓa
Tshivenḓa
-
 Sesotho sa Leboa
Sesotho sa Leboa
-
 Sesotho sa Borwa
Sesotho sa Borwa
-
 Ndumbe
Ndumbe
-
 Papuan Pidgin
Papuan Pidgin
-
 Rromani ćhib
Rromani ćhib
-
 Thok Nath
Thok Nath

News Center
News Center
HOT PRODUCT
Durable Waterproof Sheet for Subway Project Tunnel Lining
2025-09-30 08:24:56
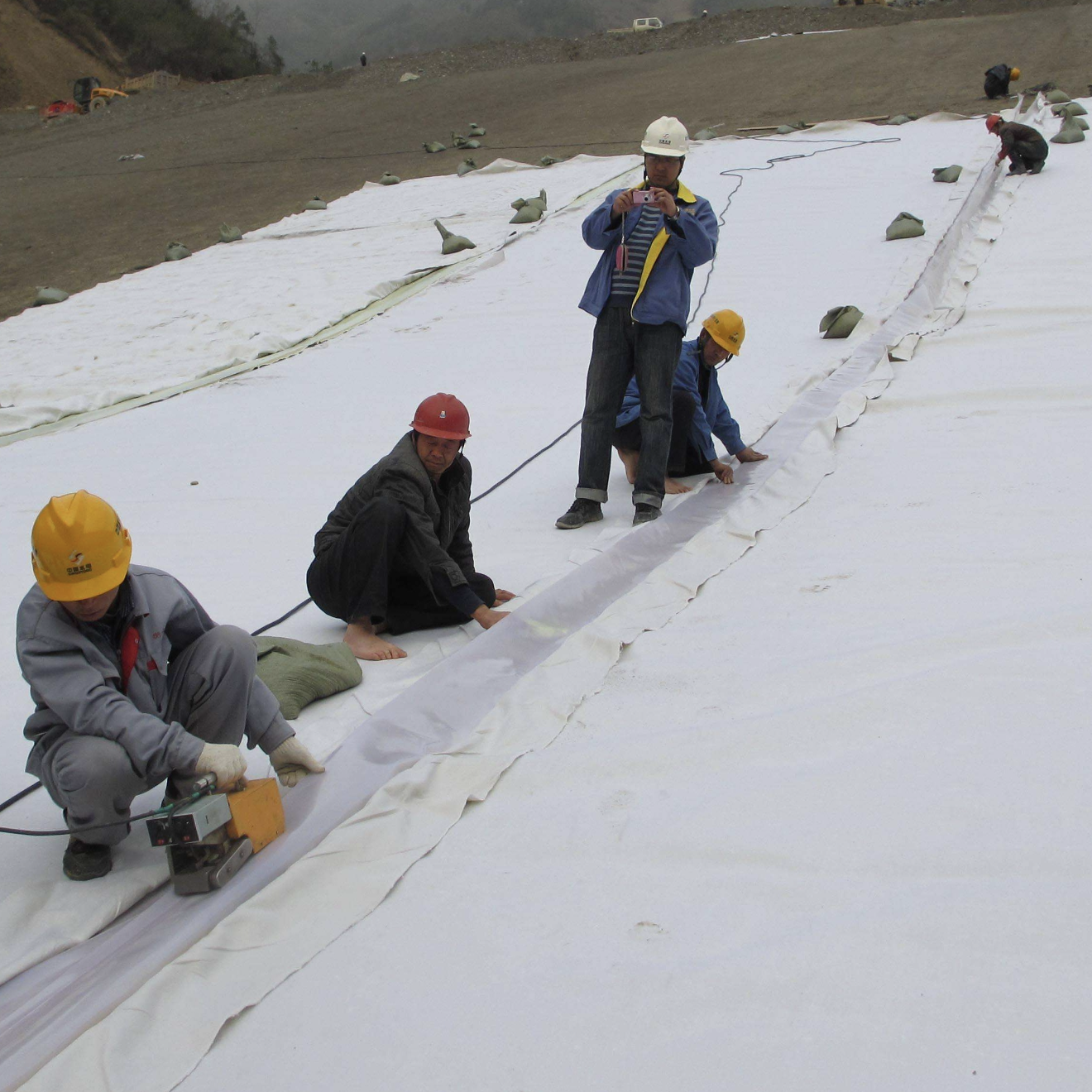

Durable Waterproof Sheet For Subway Project Tunnel Lining
Introduction
Subway systems are critical components of urban infrastructure, providing efficient and sustainable transportation solutions for millions of people worldwide. One of the most crucial aspects of subway construction is ensuring the long-term durability and waterproofing of tunnel linings. Water infiltration can lead to structural degradation, corrosion of reinforcement, and increased maintenance costs. Therefore, selecting an appropriate durable waterproof sheet is essential to protect the tunnel structure and ensure its longevity.
This paper explores the key characteristics, materials, installation methods, and performance requirements of durable waterproof sheets used in subway tunnel lining projects. It also discusses industry standards, testing protocols, and best practices to ensure optimal waterproofing performance.
---
1. Importance of Waterproofing in Subway Tunnels
1.1 Challenges in Subway Tunnel Construction
Subway tunnels are subjected to various environmental and mechanical stresses, including:
- Hydrostatic pressure from groundwater
- Chemical exposure from soil and water contaminants
- Mechanical loads from surrounding soil and train vibrations
- Temperature fluctuations affecting material expansion and contraction
Without proper waterproofing, these factors can lead to:
- Concrete deterioration due to water penetration
- Corrosion of steel reinforcements
- Mold and mildew growth, affecting air quality
- Increased maintenance and repair costs
1.2 Role of Waterproof Sheets
A durable waterproof sheet acts as a barrier between the tunnel structure and external moisture, preventing water ingress while accommodating structural movements. Key functions include:
- Preventing water infiltration into the tunnel lining
- Enhancing structural durability by protecting concrete and steel
- Reducing long-term maintenance costs
- Ensuring passenger safety and comfort
---
2. Materials for Durable Waterproof Sheets
Several materials are used in waterproof sheets for subway tunnels, each with distinct properties:
2.1 Thermoplastic Polyolefin (TPO)
- Advantages:
- High flexibility and puncture resistance
- UV and chemical resistance
- Heat-weldable seams for strong bonding
- Applications:
- Used in both exposed and buried applications
2.2 Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM)
- Advantages:
- Excellent elasticity and durability
- Resistant to extreme temperatures (-40°C to +120°C)
- Long service life (30+ years)
- Applications:
- Commonly used in waterproofing membranes for tunnels
2.3 Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
- Advantages:
- Cost-effective and widely available
- Good mechanical strength
- Easy installation with hot-air welding
- Disadvantages:
- Less flexible at low temperatures
- May contain plasticizers that degrade over time
2.4 High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- Advantages:
- High chemical and abrasion resistance
- Low permeability to water and gases
- Environmentally stable
- Applications:
- Used in geosynthetic waterproofing systems
2.5 Bituminous Membranes
- Advantages:
- Self-adhesive or torch-applied options
- Good adhesion to concrete surfaces
- Cost-effective for large-scale projects
- Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to cracking under extreme temperatures
---
3. Key Performance Requirements
A high-quality waterproof sheet for subway tunnels must meet the following criteria:
3.1 Water Resistance
- Must withstand hydrostatic pressure without leakage
- Should have low water vapor transmission rates
3.2 Durability
- Resistant to punctures, tears, and abrasion
- Long service life (minimum 25-30 years)
3.3 Flexibility & Crack Bridging
- Must accommodate structural movements without tearing
- Should bridge minor cracks in the substrate
3.4 Chemical Resistance
- Must resist degradation from soil chemicals, de-icing salts, and pollutants
3.5 Fire Resistance
- Should comply with fire safety standards to prevent tunnel fires
3.6 Ease of Installation
- Should allow for fast and secure installation with minimal seams
---
4. Installation Methods
Proper installation is critical to ensuring the effectiveness of waterproof sheets. Common methods include:
4.1 Full Adhesion Method
- The sheet is fully bonded to the substrate using adhesives or heat welding.
- Provides excellent waterproofing but requires a smooth, clean surface.
4.2 Loose-Lay Method
- The sheet is laid over the substrate and secured at edges and seams.
- Allows for movement but may be prone to punctures.
4.3 Mechanical Fixation
- Uses fasteners or battens to secure the sheet.
- Suitable for areas with high wind uplift risks.
4.4 Welding Techniques
- Hot-air welding: Used for thermoplastic sheets (PVC, TPO).
- Solvent welding: Used for EPDM and other rubber-based sheets.
4.5 Quality Control During Installation
- Seam testing: Air pressure or water penetration tests to ensure integrity.
- Visual inspection: Checking for wrinkles, bubbles, or misalignments.
---
5. Testing and Standards
Waterproof sheets must comply with international standards, including:
5.1 ASTM Standards
- ASTM D751: Testing for coated fabrics (tear strength, adhesion).
- ASTM D7928: Water vapor transmission testing.
5.2 ISO Standards
- ISO 9001: Quality management systems.
- ISO 14001: Environmental management.
5.3 EN Standards
- EN 13967: Flexible sheets for waterproofing.
- EN 14909: Plastic and rubber sheets for tunnel waterproofing.
5.4 Performance Testing
- Hydrostatic pressure test: Measures resistance to water penetration.
- Puncture resistance test: Evaluates durability under mechanical stress.
- Accelerated aging test: Simulates long-term exposure to environmental factors.
---
6. Case Studies and Best Practices
6.1 Successful Subway Tunnel Projects
- Example 1: A subway project in Europe used EPDM sheets due to their flexibility and long-term durability.
- Example 2: A project in Asia utilized HDPE geomembranes for their chemical resistance and low permeability.
6.2 Lessons Learned
- Proper surface preparation is essential for adhesion.
- Seam integrity must be rigorously tested.
- Regular maintenance inspections help detect early signs of failure.
---
7. Future Trends in Tunnel Waterproofing
7.1 Smart Waterproofing Membranes
- Integration of sensors to detect leaks in real-time.
- Self-healing materials that repair minor damages automatically.
7.2 Sustainable Materials
- Bio-based polymers with reduced environmental impact.
- Recyclable waterproofing solutions.
7.3 Advanced Installation Technologies
- Robotic welding for precise seam sealing.
- Drones for inspection of hard-to-reach areas.
---
Conclusion
Selecting the right durable waterproof sheet is crucial for the success of subway tunnel projects. Materials such as TPO, EPDM, PVC, and HDPE offer different advantages depending on project requirements. Proper installation, adherence to industry standards, and rigorous testing ensure long-term performance. As technology advances, smart membranes and sustainable materials will further enhance tunnel waterproofing solutions. By implementing best practices, engineers can ensure safe, durable, and cost-effective subway tunnel constructions for decades to come.
---
This comprehensive guide provides insights into the selection, installation, and performance of waterproof sheets in subway tunnel projects, ensuring long-term structural integrity and safety.








 Phone
Phone
Comment
(0)